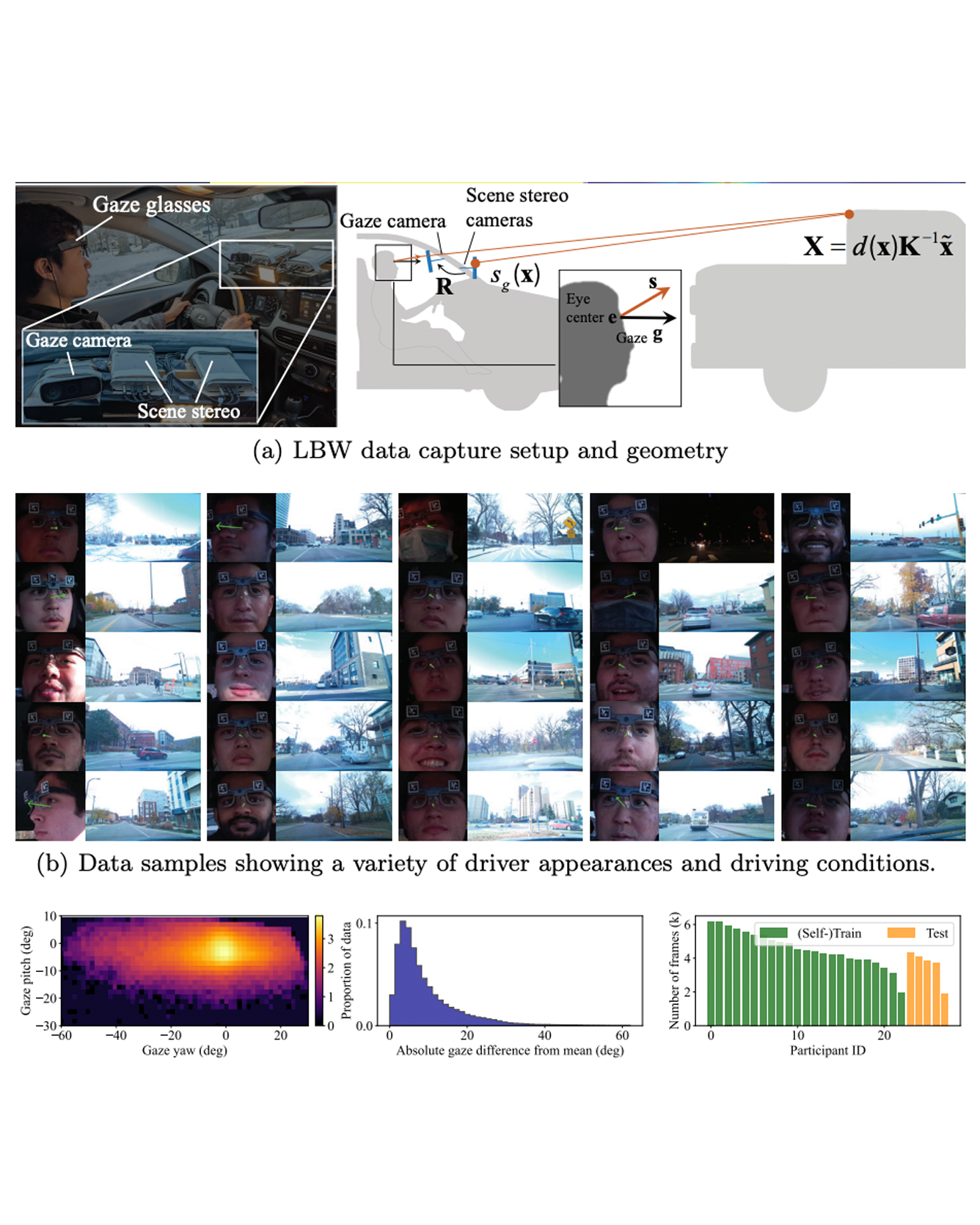
We present a new on-road driving dataset, called “Look Both Ways”, which contains synchronized video of both driver faces and the forward road scene, along with ground truth gaze data registered from eye tracking glasses worn by the drivers. Our dataset supports the study of methods for non-intrusively estimating a driver’s focus of attention while driving - an important application area in road safety. A key challenge is that this task requires accurate gaze estimation, but supervised appearance-based gaze estimation methods often do not transfer well to real driving datasets, and in-domain ground truth to supervise them is difficult to gather. We therefore propose a method for self-supervision of driver gaze, by taking advantage of the geometric consistency between the driver’s gaze direction and the saliency of the scene as observed by the driver. We formulate a 3D geometric learning framework to enforce this consistency, allowing the gaze model to supervise the scene saliency model, and vice versa. We implement a prototype of our method and test it with our dataset, to show that compared to a supervised approach it can yield better gaze estimation and scene saliency estimation with no additional labels. READ MORE


