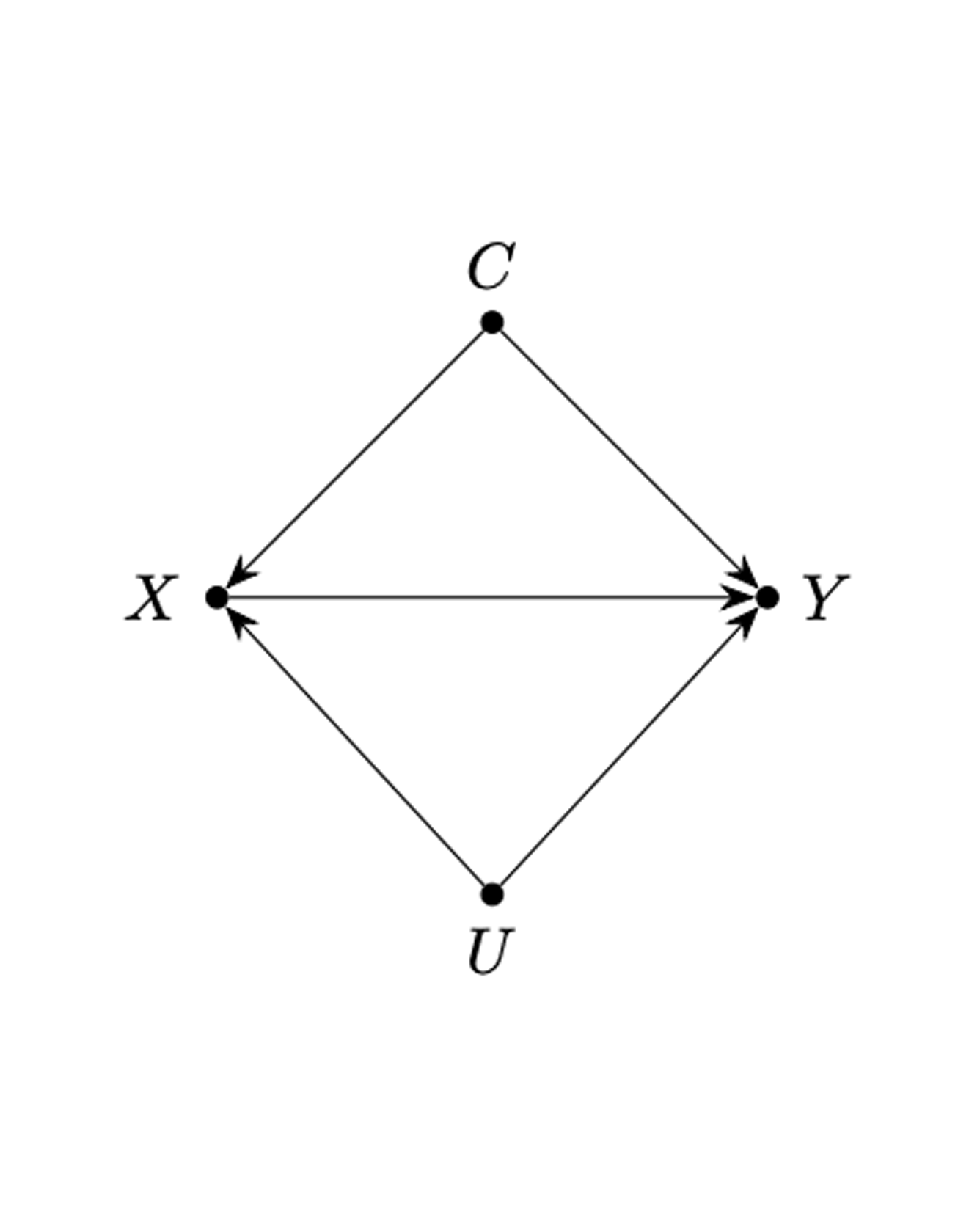
Electric vehicles (EVs) are generally considered more environmentally sustainable than internal combustion engine vehicles (ICEVs). Government and policy makers may want to incentivize multi-vehicle households who, if they purchase a new EV, would use their EV to replace a large portion of their ICEV mileage. Therefore, it is important to analyze how EV procurement affects annual EV mileage for different households. Given that many relevant data, especially experimental data, are often unavailable in the real world, we need causal analysis tools to answer this question. Additionally, our aim is to compare the expected EV mileage of different combinations of vehicles a household owns. Observing multiple combinations in an individual household is impossible since only one combination can exist, making causal inference challenging. In this paper, we construct a causal AI framework utilizing counterfactual reasoning methods to address this issue. READ MORE